Our research
Experimental System
Experiments are one of the basic methods to study the charging and electrostatic transport of lunar dust, JLPP has a complete set of vacuum plasma systems and measurement systems to support the construction of a lunar surface dust simulation environment. JLPP has established a ground-based high-vacuum‘lunar dust-solar irradiation-plasma-highspeed impact-electromagnetic field’experimental platform. It mainly includes an ultra-high vacuum chamber (diameter 1 m, length1.5 m, back pressure better than 10-4 Pa), a solar full-spectrum irradiation system (spectral range 300-1800nm, spatial inhomogeneity of irradiation:<2%, radiation intensity up to 1640 W/m2), a low-temperature plasma source (electron temperature of 1-8 eV, electron density of 1015-1018 m–3, ion velocity of 30-1000 eV), a high-speed camera, and a high-temperature plasma source (electron temperature of 1-8 eV, electron density of 1015-1018 m-3, ion velocity of 30-1000 eV). -1000 eV), high-speed camera system (resolution 1280×1024, frame rate 13600fps), simulated lunar dust (silica powder, simulated lunar dust, Geochemistry Institute simulated lunar dust), and lunar dust charged parameter measurements (piezometer, Faraday cup) system.
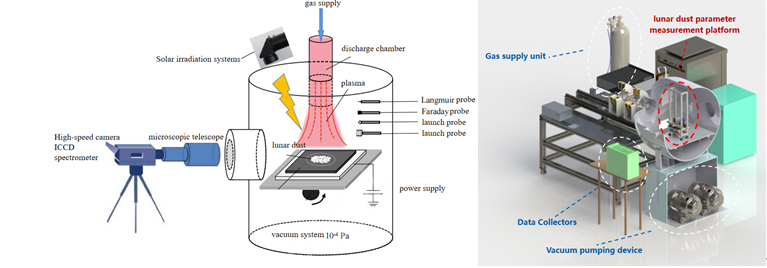
Experimental system diagram
The vacuum chamber: The vacuum chamber is a cylindrical horizontal structure with a diameter of 1m and an overall length of 1.5m. Because of the small size of the chamber, it is placed on a 60cm high platform for easy in-chamber operation. The ultimate vacuum degree is 1E-4Pa. The chamber has been grounded, shock-absorbed, anti-noise and anti-static measures.
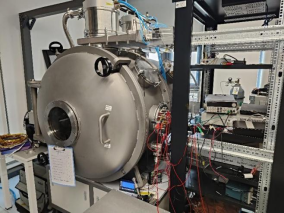
Vacuum chamber diagram
Plasma source: The LaB6 emitter on the inner wall of the cathode is heated by a 5A current, causing it to thermally dissociate and release electrons. The electrons are discharged between the emitter and the shell touching the pole (anode), ionizing the argon gas to produce a high-density plasma plume.

Hollow cathode
Electron gun ionization system: Heating the tungsten filament produces hot electron emission. The amount and energy of the electron injection can be controlled by adjusting the tungsten current strength, the tungsten-to-target spacing, and the bias voltage to the target potential.

Electron beam
langmuir probe: Measurement of plasma parameters using a langmuir probe as an indicator of the charge of dust attached to the plasma, measurements of plasma density, space potential, electron temperature, etc.

Langmuir probe
Faraday Cup: The Faraday Cup is used to measure the charge of dust particles, and with an amplifier circuit can measure charges on the order of fC.
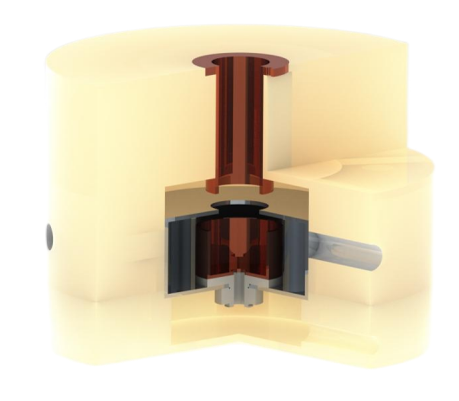
Sectional view of the Faraday Cup
(Lastly Updated in September, 2025)
