On October 14, 2021, the Long March 2D launch vehicle was successfully launched from Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center, putting the APSCO SSS-1 satellite into the predetermined orbit and making the mission a complete success. The SSS-1 satellite is the first electrospray thruster (ILT-50) developed by Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics as an auxiliary de-orbiting device, which is also the first electrospray thruster developed by a university in China to perform an in-orbit mission.
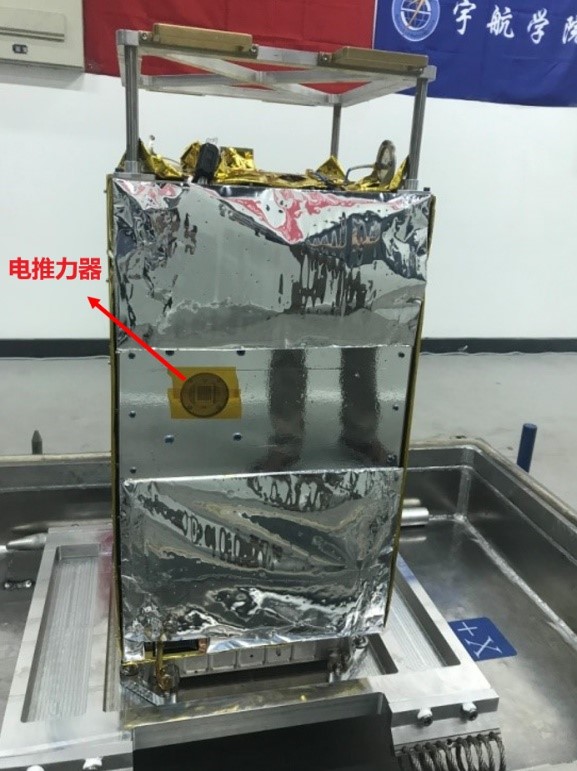
Electrospray thruster mounted on SSS-1 satellite
The ILT-50 electrospray thruster was developed by the team of Prof. Tang Haibin, Prof. Yang Lijun and Prof. Liu Yu in the School of Astronautics. The electrospray thruster involves research in multiple disciplines such as seepage physics, spray mechanism, electrochemistry and field emission effects, and is an international research hotspot and frontier in the field of space propulsion. With low power consumption, compact structure, flexible control and high reliability, electrospray thrusters provide new solutions for active reorbiting and attitude control of micro-nano-satellites, which can realize the tasks of micro-nano-satellite networking and formation flight, drag-free control, precise positioning and earth observation of spacecraft, and are of great significance to the development and application of space technology.
During the development of ILT-50 electrospray thruster, the student project team proposed the theory of electro-atomization dynamics under the action of non-constant electric field, broke through the key technologies of thruster self-neutralization, thruster/power supply integration and accurate measurement of micro-newton level thrust, and realized the self-neutralization work of a single electrospray thruster by capacitive power storage for the first time in the world and applied it to satellite missions in orbit.
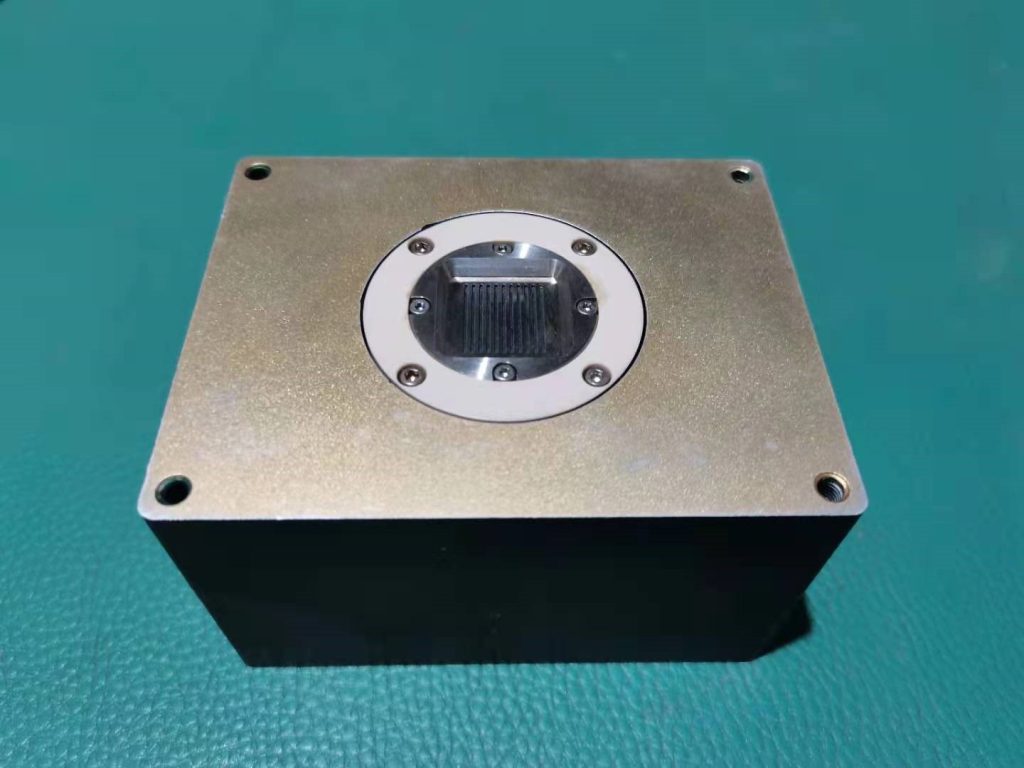

ILT-50 electrospray thruster (integrated thruster/power supply module)

ILT-50 thruster and its ignition plume
The development team of ILT-50 electrospray thruster is mainly composed of several master and doctoral students and their instructors from the School of Astronautics. With the support of the leadership of the School and the overall technical team of SSS-1 satellite, the development team has successfully completed the design, testing, optimization of the prototype and initial prototype thruster, as well as the processing, testing and delivery of the prototype product, laying a solid foundation for the realization of the deorbiting function of SSS-1 satellite.
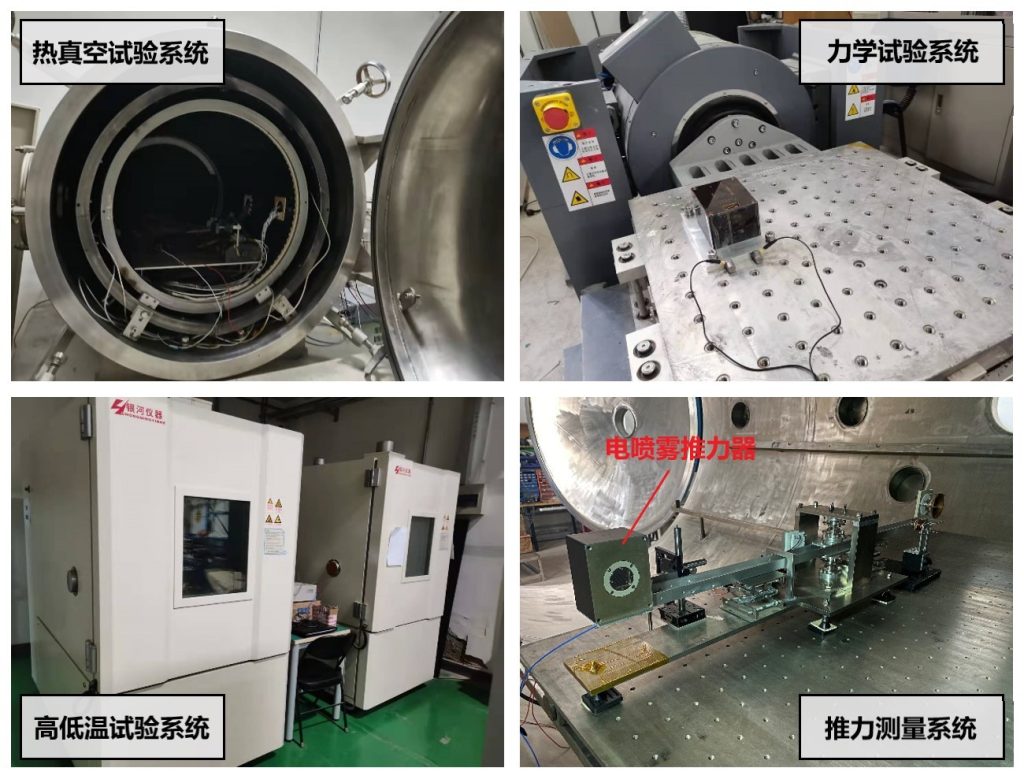

Electrospray thrusters perform environmental tests and micro-thrust measurement tests
Article: Ruojian Pan
Photo: Kunlong Wu
